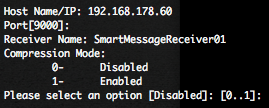
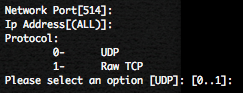
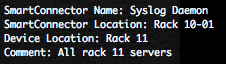
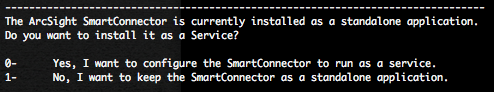
Cisco has release, the 26 September 2012, during his bi-annual Security Advisory Bundle, 9 security bulletins dealing with 8 vulnerabilities. Eight of the advisories address vulnerabilities in Cisco IOS Software, and one advisory addresses a vulnerability in Cisco Unified Communications Manager.
cisco-sa-20120926-bgp – Cisco IOS Software Malformed Border Gateway Protocol Attribute Vulnerability
cisco-sa-20120926-bgp is concerning Cisco IOS, IOS-XR and Cisco IOS-XE Softwares how contains a vulnerability in the Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) routing protocol feature. Repeated exploitation of the vulnerability could lead to inability to route packets to BGP neighbors during reconvergence times.
The vulnerability is identified as CVE-2012-4617, with a CVSS base score of 7.1, and was internally discovered by Cisco during testing.
cisco-sa-20120926-ios-ips – Cisco IOS Software Intrusion Prevention System Denial of Service Vulnerability
cisco-sa-20120926-ios-ips is concerning Intrusion Prevention System (IPS) feature present in Cisco IOS Software. An unauthenticated, remote attacker could cause a reload of an affected device.
The vulnerability is identified as CVE-2012-3950, with a CVSS base score of 7.8, and was discovered when handling customer support requests.
cisco-sa-20120926-nat – Cisco IOS Software Network Address Translation Vulnerabilities
cisco-sa-20120926-nat is concerning Cisco IOS Software Network Address Translation (NAT) how contains two denial of service (DoS) vulnerabilities.
CVE-2012-4618 and CVE-2012-4619 vulnerabilities have both a CVSS base score of 7.8, and were discovered during troubleshooting of TAC service requests.
cisco-sa-20120926-c10k-tunnels – Cisco IOS Software Tunneled Traffic Queue Wedge Vulnerability
cisco-sa-20120926-c10k-tunnels is concerning Cisco IOS Software on Cisco 10000 Series router how contains a vulnerability when processing IP tunneled packets. This vulnerability could lead to denial of service (DoS).
The vulnerability is identified as CVE-2012-4620, with a CVSS base score of 7.8, and was discovered during troubleshooting of a customer issue.
cisco-sa-20120926-dhcpv6 – Cisco IOS Software DHCP Version 6 Server Denial of Service Vulnerability
cisco-sa-20120926-dhcpv6 is concerning Cisco IOS Software and Cisco IOS XE Software how contain a vulnerability how could lead to denial of service (DoS).
The vulnerability is identified as CVE-2012-4623, with a CVSS base score of 7.1, and was discovered by Cisco during internal testing.
cisco-sa-20120926-ecc – Cisco Catalyst 4500E Series Switch with Cisco Catalyst Supervisor Engine 7L-E Denial of Service Vulnerability
cisco-sa-20120926-ecc is concerning Catalyst 4500E series switch with Supervisor Engine 7L-E how contain a vulnerability how could lead to denial of service (DoS).
The vulnerability is identified as CVE-2012-4622, with a CVSS base score of 7.8, and was discovered when handling customer service requests.
cisco-sa-20120926-dhcp – Cisco IOS Software DHCP Denial of Service Vulnerability
cisco-sa-20120926-dhcp is concerning Cisco IOS Software how contain a vulnerability how could lead to denial of service (DoS).
The vulnerability is identified as CVE-2012-4621, with a CVSS base score of 7.8, and was discovered during the troubleshooting of customer service requests.
cisco-sa-20120926-cucm – Cisco Unified Communications Manager Session Initiation Protocol Denial of Service Vulnerability
cisco-sa-20120926-cucm is concerning Cisco Unified Communications Manager how contains a vulnerability in its Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) implementation. This vulnerability could lead to denial of service (DoS).
The vulnerability is identified as CVE-2012-3949, with a CVSS base score of 7.8, and was discovered during troubleshooting of TAC service requests.
cisco-sa-20120926-sip – Cisco IOS Software Session Initiation Protocol Denial of Service Vulnerability
cisco-sa-20120926-sip is concerning Cisco IOS Software and Cisco IOS XE Software how contains a vulnerability in there Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) implementation. This vulnerability could lead to denial of service (DoS).
The vulnerability is identified as CVE-2012-3949, with a CVSS base score of 7.8, and was discovered during troubleshooting of TAC service requests.