If you are projecting to start a Log or Event Management project, you will surely need to know your Normal Event log size (NE). These Normal Event log size (NE) value, combinated with the your Normal Events per second (NE) value and with your storage retention policy will help you to design in order to estimate your storage requirements.
Never forget that Log Management storage requirements are not the same for Event Management. Most of time Log Management storage requirements are higher than for Event Management. For example for Log Management, PCI-DSS v2.0 Req. 10.7 require 1 year retention :
10.7 Retain audit trail history for at least one year, with a minimum of three months immediately available for analysis (for example, online, archived, or restorable from back-up).
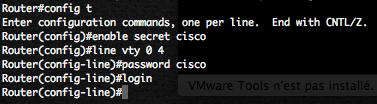
But in order to compensate PCI-DSS v2.0 Req. 10.6, you will maybe do Event Management with a SIEM (like ArcSight ESM, RSA enVision, QRadar SIEM, etc.).
10.6 Review logs for all system components at least daily. Log reviews must include those servers that perform security functions like intrusion-detection system (IDS) and authentication, authorization, and accounting protocol (AAA) servers (for example, RADIUS). Note: Log harvesting, parsing, and alerting tools may be used to meet compliance with Requirement 10.6
You don’t need a SIEM to do Log Management, but you also don’t need to store 1 year of your logs on your SIEM solution. Long term retention, long term reporting, “raw” events forensics are mostly done on a Log Management infrastructure (like ArcSight Logger, QRadar Log Manager, Novell Sentinel Log Manager, etc.). Storage retention for your Event Management infrastructure will depend mostly on your correlation rules, your acknowledge time on a correlated event, the number of security analysts present in your SOC, etc.
Don’t imagine that a magic formula exist to define your events log size, some tools could help you, but you need to analyze your logs in order to have your Normal Event log size. First of all you have to define your Log and/or Event Management scope, this scope could first be driven by regulations or compliances, but don’t forget that regulations or compliances are not Security. Also each technologies have different log sizes, an Apache HTTPD log will not have the same size than a SSHD log, and an Apache HTTPD log from server A will surely not have the same size than an Apache HTTPD log from server B.
xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx - - [25/Aug/2011:04:23:47 +0200] "GET /feed/ HTTP/1.1" 304 - "-" "Apple-PubSub/65.28"
This log from Apache HTTPD server A has a size of 102 bytes.
xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx - - [25/Aug/2011:04:15:08 +0200] "GET /wp-content/themes/mystique/css/style-green.css?ver=3.0.7 HTTP/1.1" 200 1326 "http://eromang.zataz.com/" "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; en-US; rv:1.9.2.20) Gecko/20110803 Firefox/3.6.20 ( .NET CLR 3.5.30729)"
This log from Apache HTTPD server B has a size of 274 bytes.
Also, depending the Log or Event Management infrastructure product, you need to consider event generated by intrinsically mechanism. For example, in order to search in your events most of products are creating indexes, these indexes are representing an average of twice the time of the size of the event. Also another intrinsically mechanism is that these products are also monitoring themselves, regularly executing tasks, do some statistics for dashboards or reports.
I have develop a bash script how will permit you to analyze all your archived logs and gather the following informations:
- For each archived files, the total number of events, the total uncompressed size of the events, the Normal Event log size.
- The total events for all archived files.
- The total uncompressed size of all events in all archived files.
- The grant total Normal Event log size.
- The average event number per archived files.
- The average bytes per archived file.
You can download this script by clicking on this link. A reminder, the provided Normal Events per second value, is not your real EPS rate, just check my previous blogpost regarding on “Why and howto calculate your Events Per Second“.