The Metasploit Team has release a new plugin, a bridge between Metasploit and Nessus. This new plugin is a collaboration between HD Moore, James Lee, Zate Berg, darkoperator and the Nessus Team. If you follow the PaulDotCompodcast, you know that Paul is a employe of the Nessus team and that darkoperator (aka Carlos Perez) is an official developer of the Metasploit project. A good collaboration between the 2 teams how has uncorked on this new important step in Metasploit.
In the first par of the post serie, we have describe all the generic, user and policy command. In this new post we will describe the plugin, scan, report and “nessus_find_targets” commands.
Plugin Commands
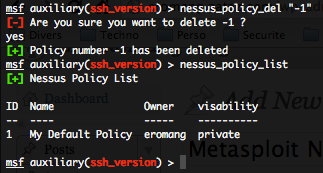
- Getting a list of plugins by family – nessus_plugin_list :
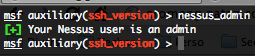
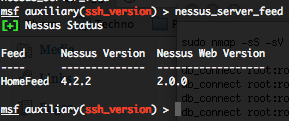
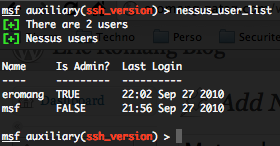
If you are an admin user or a normal user, by typing this command you will have a list of plugins by family.
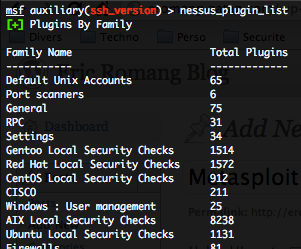
- Getting the detail of a family of plugins – nessus_plugin_family :
If you wish to have the detail of a plugin family, just type the following command :
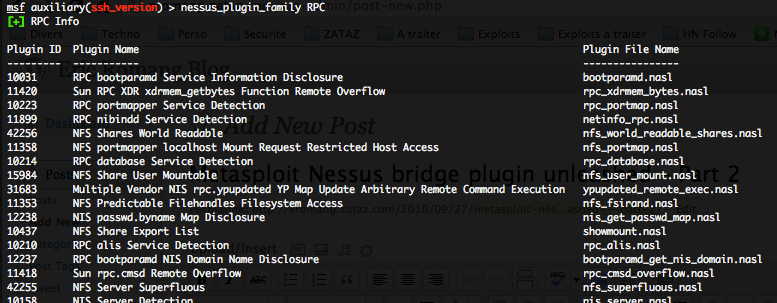
- Getting details on a specific plugin of a family – nessus_plugin_details :
To get details on a specific plugin of a family of plugin, you have to precise the plugin file name listed with the previous “nessus_plugin_family” command.
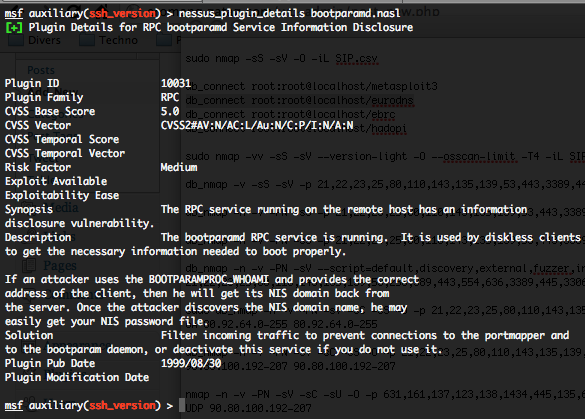
- Details of Nessus plugins preferences – nessus_plugin_prefs :
To get details of all Nessus plugins preferences, just type the following command :
nessus_plugin_prefs
Scan Commands
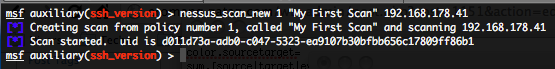
- Starting a new Nessus scan – nessus_scan_new :
To start a new Nessus scan run the following command :
nessus_scan_new <policy id> <scan name> <targets>
Where “policy id” is the unique ID of the policy to be used, “scan name” the name of the scan and “targets” the targeted hostnames or IP addresses.
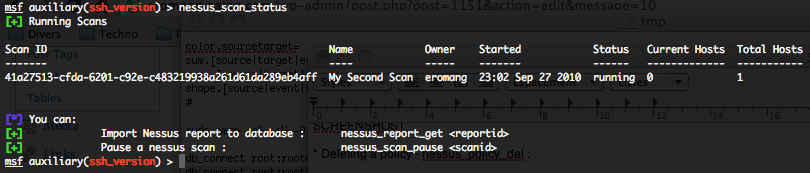
- List of all current Nessus scans – nessus_scan_status :
To get a list of all current Nessus scans, run the following command :
- Pausing a running Nessus scan – nessus_scan_pause :
To pause a running Nessus scan run the following command :
nessus_scan_pause <scan id>
Where “scan id” is the unique ID of the Nessus scan how is available by the previous command “nessus_scan_status“.

To pause all running Nessus scans, just run the following command :
nessus_scan_pause_all
- Resuming a paused Nessus scan – nessus_scan_resume :
To resume a Nessus scan run the following command :
nessus_scan_resume <scan id>
Where “scan id” is the unique ID of the Nessus scan how is available by the command “nessus_scan_status“.

To resume all paused Nessus scans, just run the following command :
nessus_scan_resume_all
- Stopping a Nessus scan – nessus_scan_stop :
To stop a Nessus scan, run the following command :
nessus_scan_stop <scan id>
Where “scan id” is the unique ID of the Nessus scan how is available by the command “nessus_scan_status“.

To stop all the Nessus scan, just type the following command :
nessus_scan_stop_all
In the following post we will describe the reports and the “nessus_find_targets” commands.