Metasploit provide some VMware auxiliary modules who will permit you to fingerprint, gather information’s, enumerate users/groups/permissions, enumerate or terminate user administrative sessions, enumerate virtual machines hosted on ESX/ESXi and power on/off virtual machines.
You can find all these auxiliary modules through the Metasploit search command.
VMWare ESX/ESXi Fingerprint Scanner (esx_fingerprint)
To invoke this auxiliary module just type the following command :
This module attempt try to access to VMware ESX/ESXi Web API interfaces and attempts to identify the running version of ESX/ESXi. Web API interfaces are running on port 443/TCP with “/sdk” default URL, also all connections are encrypted in SSL.
You can run this module against multiple hosts by defining the “RHOSTS” variable. “RHOSTS” variable could be a unique IP address, an IP addresses range (ex : 192.168.1.0-192.168.1.255, or 192.168.1.0/24) or a file (ex : file:/tmp/ip_addresses.txt). Also in order to parallelize brute force attempts, just increase the number of concurrent threads by setting the “THREADS” variable.
VMWare Authentication Daemon Version Scanner (vmauthd_version)
To invoke this auxiliary module just type the following command :
This module will gather information’s about an ESX/ESXi host through the vmauthd service on port 902/TCP.
You can run this module against multiple hosts by defining the “RHOSTS” variable. “RHOSTS” variable could be a unique IP address, an IP addresses range (ex : 192.168.1.0-192.168.1.255, or 192.168.1.0/24) or a file (ex : file:/tmp/ip_addresses.txt). Also in order to parallelize brute force attempts, just increase the number of concurrent threads by setting the “THREADS” variable.
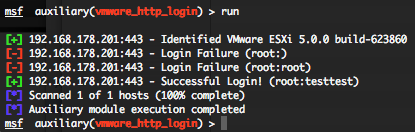
VMWare Web Login Scanner (vmware_http_login)
To invoke this auxiliary module just type the following command :
This module attempts to authenticate to the VMWare HTTP service for VmWare Server, ESX, and ESXi.
You can run this module against multiple hosts by defining the “RHOSTS” variable. “RHOSTS” variable could be a unique IP address, an IP addresses range or a file. This module is also attempting to authenticate using username and password combinations indicated by the “USER_FILE“, “PASS_FILE“, and “USERPASS_FILE” options. You can use SkullSecurity password lists. Also in order to parallelize brute force attempts, just increase the number of concurrent threads by setting the “THREADS” variable.
All valid user and password combinations are in green, invalid login are in red.
VMWare Authentication Daemon Login Scanner (vmauthd_login)
To invoke this auxiliary module just type the following command :
This module will test vmauthd logins on a range of machines and report successful logins.
You can run this module against multiple hosts by defining the “RHOSTS” variable. “RHOSTS” variable could be a unique IP address, an IP addresses range or a file. This module is also attempting to authenticate using username and password combinations indicated by the “USER_FILE“, “PASS_FILE“, and “USERPASS_FILE” options. You can use SkullSecurity password lists. Also in order to parallelize brute force attempts, just increase the number of concurrent threads by setting the “THREADS” variable.
All valid user and password combinations are in green, invalid login are in red.
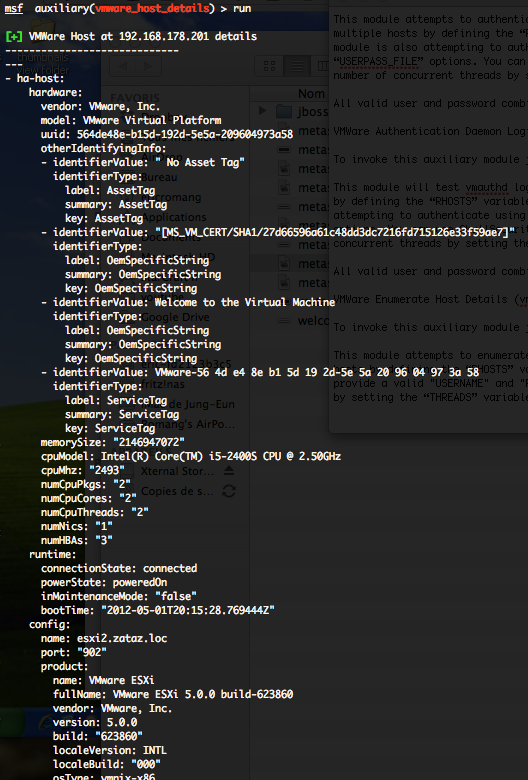
VMWare Enumerate Host Details (vmware_host_details)
To invoke this auxiliary module just type the following command :
This module attempts to enumerate information about the host systems through the VMWare web API.
You can run this module against multiple hosts by defining the “RHOSTS” variable. “RHOSTS” variable could be a unique IP address, an IP addresses range or a file. You have to provide a valid “USERNAME” and “PASSWORD“. In order to parallelize brute force attempts, just increase the number of concurrent threads by setting the “THREADS” variable. Also, you can enumerate hardware details of the host by setting the “HW_DETAILS” option to “true“.
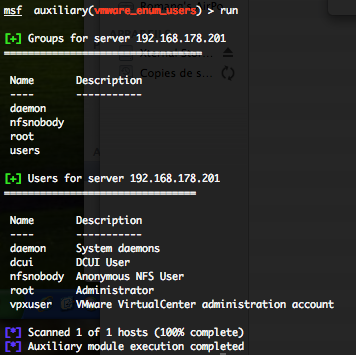
VMWare Enumerate User Accounts (vmware_enum_users)
To invoke this auxiliary module just type the following command :
This module will log into the Web API of VMWare and try to enumerate all the user accounts. If the VMware instance is connected to one or more domains, it will try to enumerate domain users as well.
You can run this module against multiple hosts by defining the “RHOSTS” variable. “RHOSTS” variable could be a unique IP address, an IP addresses range or a file. You have to provide a valid “USERNAME” and “PASSWORD“. Also, in order to parallelize brute force attempts, just increase the number of concurrent threads by setting the “THREADS” variable.
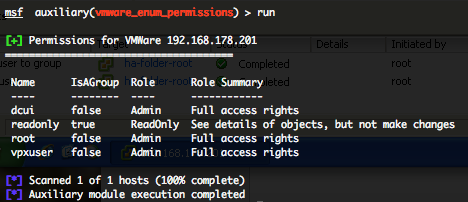
VMWare Enumerate Permissions (vmware_enum_permissions)
To invoke this auxiliary module just type the following command :
This module will log into the Web API of VMWare and try to enumerate all the user/group permissions. Unlike “vmware_enum_users” auxiliary module this is only users and groups that specifically have permissions defined within the VMware product.
You can run this module against multiple hosts by defining the “RHOSTS” variable. “RHOSTS” variable could be a unique IP address, an IP addresses range or a file. You have to provide a valid “USERNAME” and “PASSWORD“. Also, in order to parallelize brute force attempts, just increase the number of concurrent threads by setting the “THREADS” variable.
VMWare Enumerate Active Sessions (vmware_enum_sessions)
To invoke this auxiliary module just type the following command :
This module will log into the Web API of VMware and try to enumerate all the login sessions.
You can run this module against multiple hosts by defining the “RHOSTS” variable. “RHOSTS” variable could be a unique IP address, an IP addresses range or a file. You have to provide a valid “USERNAME” and “PASSWORD“. Also, in order to parallelize brute force attempts, just increase the number of concurrent threads by setting the “THREADS” variable.
Unfortunately this module is not working with VMware ESXi 5.0
VMWare Terminate ESX Login Sessions (terminate_esx_sessions)
To invoke this auxiliary module just type the following command :
This module will log into the Web API of VMWare and try to terminate user login sessions as specified by the session keys.
You can run this module against one host by defining the “RHOST” variable. You have to provide a valid “USERNAME” and “PASSWORD“. Also you have to provide a session key identified by the previous “vmware_enum_sessions” auxiliary module by defining the “KEYS” variable.
Unfortunately this module is not working with VMware ESXi 5.0
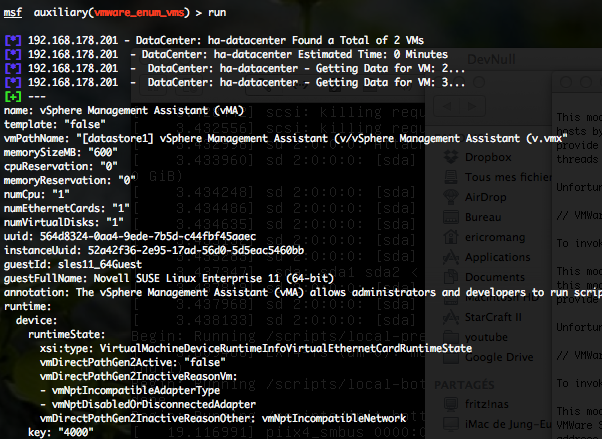
VMWare Enumerate Virtual Machines (vmware_enum_vms)
To invoke this auxiliary module just type the following command :
This module attempts to discover virtual machines on any VMWare instance running the web interface. This would include ESX/ESXi and VMWare Server.
You can run this module against multiple hosts by defining the “RHOSTS” variable. “RHOSTS” variable could be a unique IP address, an IP addresses range or a file. You have to provide a valid “USERNAME” and “PASSWORD“. Also, in order to parallelize brute force attempts, just increase the number of concurrent threads by setting the “THREADS” variable. By defining the “SCREENSHOT” variable, the auxiliary module will try to take a screenshot of the running VM.
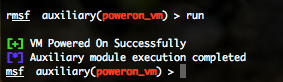
VMWare Power On Virtual Machine (poweron_vm)
To invoke this auxiliary module just type the following command :
This module will log into the Web API of VMWare and try to power on a specified Virtual Machine.
You can run this module against one host by defining the “RHOST” variable. You have to provide a valid “USERNAME” and “PASSWORD“. Also you have to provide a virtual machine name identified by the previous “vmware_enum_vms” auxiliary module by defining the “VM” variable (for example : set VM CentOS 5.8 i386).
VMWare Tag Virtual Machine (tag_vm)
To invoke this auxiliary module just type the following command :
This module will log into the Web API of VMWare and ‘tag’ a specified Virtual Machine. It does this by logging a user event with user supplied text.
You can run this module against one host by defining the “RHOST” variable. You have to provide a valid “USERNAME” and “PASSWORD“. You have to provide a virtual machine name identified by the previous “vmware_enum_vms” auxiliary module by defining the “VM” variable (for example : set VM CentOS 5.8 i386). Also you have to provide a message through the “MSG” variable.
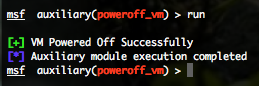
VMWare Power Off Virtual Machine (poweroff_vm)
To invoke this auxiliary module just type the following command :
This module will log into the Web API of VMWare and try to power off a specified Virtual Machine.
You can run this module against one host by defining the “RHOST” variable. You have to provide a valid “USERNAME” and “PASSWORD“. Also you have to provide a virtual machine name identified by the previous “vmware_enum_vms” auxiliary module by defining the “VM” variable (for example : set VM CentOS 5.8 i386).