In my previous blob posts I have explain on how to install ArcSight Logger L750MB, how to setup a Windows Snare SmartConnector, some useful ArcSight SmartConnector commands and on how to backup your Logger configurations. This new blog post will explain you on how to setup a Cisco lab with Dynamips and Dynagen and how to setup an ArcSight Cisco IOS SmartConnector. The ArcSight Cisco IOS SmartConnector supports 2600 series and above with IOS 11.3, 12.4, 15.0, and 15.1.
Dynamips and Dynagen lab setup
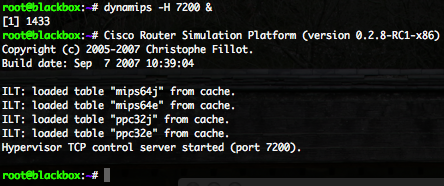
First of all my lab is running under Ubuntu 10.04.2 LTS. Dynamips is a Cisco router emulator, but he can also emulate switches and Cisco PIX/ASA. Dynagen is a front-end for Dynamips. “Dynagen takes care of specifying the right port adapters, generating and matching up those pesky NIO descriptors, specifying bridges, frame-relay, ATM switches, etc. It also provides a management CLI for listing devices, suspending and reloading instances, determining and managing idle-pc values, performing packet captures, etc.”.
You have to create a “dynamics” folder into your “/opt” directory.
Download the latest Dynagen version and uncompress the archive in the “dynamips” folder. My lab Dynagen version is 0.9.1 and this specific version require at least version 0.2.8-RC1 of Dynamics. Download version 0.2.8-RC1 of Dynamics and use the “chmod 755” command to make the Dynamips binary executable.
Create symbolic links, in “/usr/sbin” for the Dynagen and Dynamips programs.
cd /usr/sbin
ln -s /opt/dynamips/dynagen-0.11.0/dynagen dynagen
ln -s /opt/dynamips/dynamips-0.2.8-RC1-x86.bin dynamips
Create a directory for Cisco IOS images.
Download you Cisco IOS images into the “images” directory. To find Cisco IOS images you can use some Google dorks.
For 7200 search with intitle:index.of c7200*.bin -site:cisco.com – Try
For 3660 search with intitle:index.of c3660*.bin -site:cisco.com – Try
For PIX search with intitle:index.of cisco pix*.bin -site:cisco.com – Try
For my lab I have use the “c7200-adventerprisek9-mz.124-4.T1.bin” IOS image. You will maybe need to uncompress the IOS image archive.
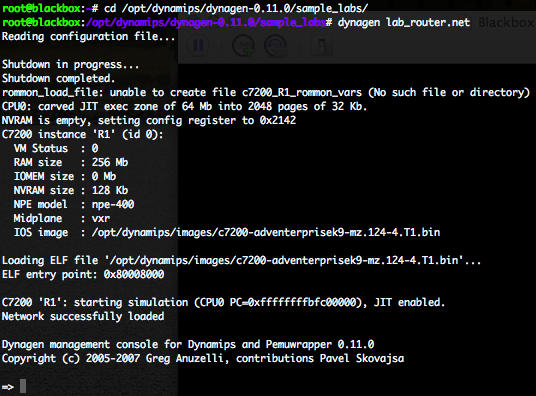
Then create a “lab_router.net” file into “/opt/dynamips/dynagen-0.11.0/sample_labs” directory. Here under my “lab_router.net” configuration.
[localhost]
[[7200]]
ram=256
image = /opt/dynamips/images/c7200-adventerprisek9-mz.124-4.T1.bin
nep = npe-400
[[router R1]]
model = 7200
f0/0 = NIO_tap:tap0
f1/0 = NIO_gen_eth:eth0
Maybe you have to adapt your IOS image file path.
Now you have to create a TUN/TAP interface on your Linux box.
Install “uml-utilities” package.
Load the TUN/TAP driver into the kernel.
Create a TUN/TAP interface by invoking the “tunctl” command. Enable the “tap0” interface and configure an IP address for it.
Remove your existing “eth0” interface configuration with the following command.
Add a default route that points to the router interface connected to the “tap0” interface.
Now start the dynamics process with the following command. Not that the “&” character instruct the process to run in the background.
Use the “dynagen” command to process the “lab_router.net” configuration file and start the virtual network.
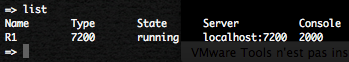
The Dynagen “list” command will permit you to list the network equipment and the the TCP port for console access.
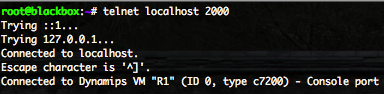
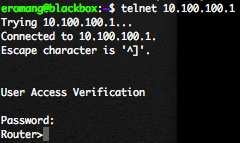
Connect you with telnet on “localhost” port “2000” to get access to the router.
On the first router configuration question response “no“.
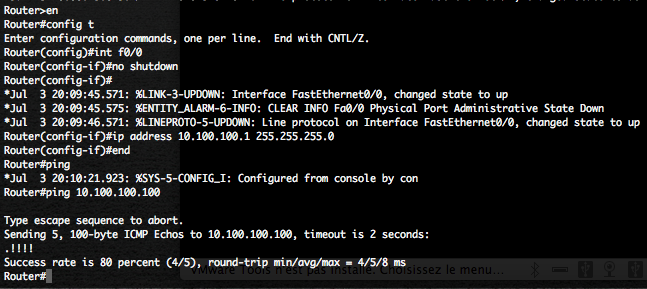
Perform the following tasks on the router, to configure the “f0/0” router interface how is mapped to the TUN/TAP “tap0” interface.
- Enter in configuration mode.
- Enable the “f0/0” interface
- Provide an IP address for this interface
- Try to ping the “tap0” interface
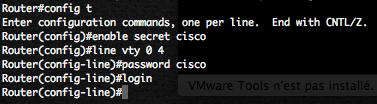
Now provide Cisco passwords.
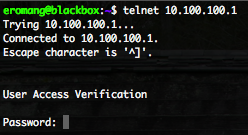
At this point you can connect you, with telnet, from the Linux box to the Cisco router directly on IP 10.100.100.1.
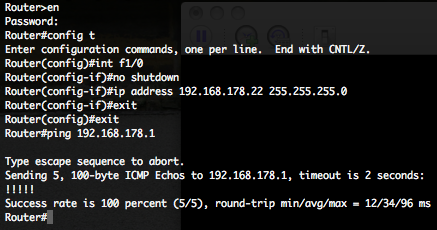
Perform the following tasks on the router, to finish our router configuration to have the possibility to communicate with external world.
- Enter in configuration mode.
- Enable the “f1/0” interface
- Provide an IP address for this interface, here 192.168.178.22.
- Try to ping the default gateway for 192.168.178.0/24 network, here 192.168.178.1.
Your Cisco router is now able to communicate with outside world.
ArcSight Cisco IOS SmartConnector installation and setup
If you have an existing Syslog UDP daemon, for example the SmartConnector configured in the Snare Windows blog post, you don’t need to follow the installation and setup. ArcSight Cisco IOS SmartConnector is considered as a “sub connector” for Syslog SmartConnector. All Cisco IOS messages how will be received by the Syslog UDP daemon are recognized coming from a Cisco IOS, but the same Syslog UDP daemon can also receive Windows Snare, Snort, Juniper NSM, JunOS, Red Hat Linux Audit messages. Cisco IOS Syslog message will be converted into SmartMessage (CEF) format.
First verify that you don’t have any existing Syslog UDP daemon how is running on the box, you can use “netstat -uan” to verify this.
Upload the “ArcSight-5.0.2.5703.0-Connector-Downloadable-Logger-Linux.bin” binary available from the ArcSight Download Center, and use the “chmod 755” command to make the binary executable.
Execute the binary in order to install the SmartConnector.
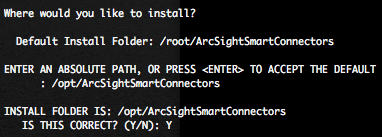
Press “Enter” twice times, provide the installation directory, in our case “/opt/ArcSightSmartConnectors” and confirm the installation.
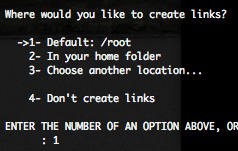
We recommend you to create a links in order to remove the SmartConnector.
Once the SmartConnector installed you need to configure him.
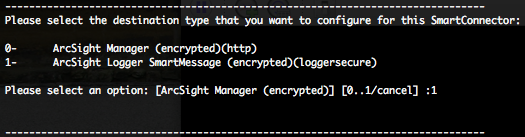
Select the destination type that you want to configure for this SmartConnector, in our case it will be the L750MB Logger.
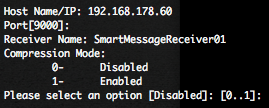
Provide the hostname or IP address of the Logger, the destination port (for Logger software version the port is 9000/TCP), and the Receiver Name (available in the Configuration -> Event Input / Output menu of the Logger).
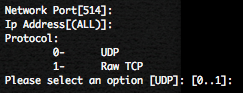
Select “Syslog Daemon(syslog)” as SmartConnector to install, don’t change the network IP, port and protocol (514/UDP).
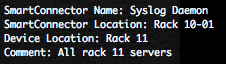
Provide a SmartConnector name, don’t forget that the SmartConnector could also receive Syslog messages from other devices than Cisco IOS.
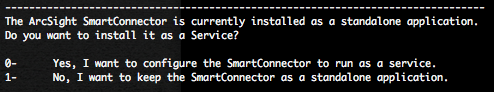
Select if you want to install the SmartConnector as a service or as a standalone application, in our case we will stay in standalone mode.
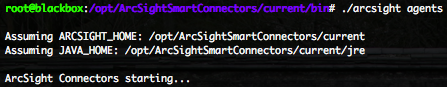
Now you have to start the SmartConnector by executing the following commands.
The SmartConnector is waiting for messages and is running (ET=Up, HT=Up).
Configure Cisco IOS for event collection
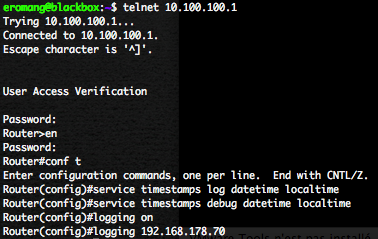
Log again on the Cisco router with telnet.
Execute the following steps to enable Cisco IOS event collection.
- Enter in enable mode.
- Enter in configuration mode.
- Enable Time-Stamps on Log Message
- Enable System Message Loggin
- Set the Syslog Destination, in our case the Syslog UDP daemon SmartConnector.
In your ArcSight SmartConnector console, you will see that the first Cisco vendor and CiscoRouter product message has been received by the SmartConnector.
Also if you check the “/opt/ArcSightSmartConnectors/current/logs/agent.log” log file, you will see these messages.
[2011-07-03 21:20:33,717][INFO ][default.com.arcsight.agent.loadable._EventCounter][processSingleAlert] First event from [CISCO|CiscoRouter||192.168.178.22] received.
[2011-07-03 21:20:38,033][INFO ][default.com.arcsight.common.eb.a][processSingleAlert] Succesfully loaded categorization file [cisco/ciscorouter_xr.csv]
[2011-07-03 21:20:45,419][INFO ][default.com.arcsight.agent.loadable._DeviceEventCounter][processSingleAlert] New device found [|192.168.178.22|CISCO|CiscoRouter]. Starting counters.
In your Logger you will see all Cisco events.